There’s a double blow to our ringing plans this weekend. Number One is the weather with a Red weather warning of severe winds up to 70mph over northern Britain as Storm Arwen passes over in a north to south direction. Sat here in my office there’s a hoolie blowing and I’m not for going anywhere until Monday when the winds should ease.
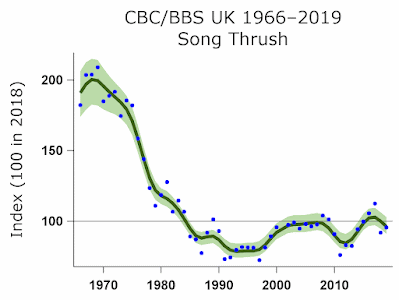
Wednesday saw another visit to Project Linnet where Catch of the Day was that extreme rarity - a Song Thrush. After a little levelling off in recent years the graph seems to be heading in a downward direction again via “a rapid decline in England” - BTO Bird Trends.
For what it’s worth the decline in this part of Lancashire seems especially marked where the Song Thrush is no longer a garden bird and is one that receives barely a mention on local bird news Internet sites. Our own catches of Song Thrushes number so few that catching a Song Thrush becomes a Red Letter Day.
Song Thrush
In addition to the single Song Thrush we caught 1 Redwing, 2 “continental” Blackbirds, 2 Blue Tit, 1 Greenfinch, 1 Robin and added another seven Linnets to our totals.
Just as were looked forward to better weather next week, Friday morning brought unwelcome Blow Number Two.
“Dear Philip”
“Avian influenza H5N1 (pathogenicity to be confirmed) has been found in a premises near Poulton le Fylde, Wyre, Lancashire. A 3km and 10km Control Zone has been put in place around the premises. Please see the map here for more information (search on SD3748).
You are being notified as we can see you, or your ringing group, have either submitted ringing records from close to the outbreak in recent years or your postal address is within the area.
Effective immediately, as a precaution, the following measures apply:
All ringing is suspended within the 10 km Control Zone as outlined on the map until further notice.
We will inform you by email when ringing can recommence and we will be monitoring the situation during the BTO Christmas period.”
A couple of our local ringing sites fall into the exclusion zone, another unwanted blow to our commitment to local bird ringing, activities that monitor bird populations for the benefit of society as a whole. Project Linnet (and farmland birds) is now on hold until sometime in 2022.
This latest episode is the third recorded outbreak of bird flu at the same Preesall/Pilling premises https://anotherbirdblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/a-touch-of-flu.html
Once again in 2021 the avian virus has been found where Pheasants, Red-legged Partridge and Mallards are reared in captivity so as to be released into the countryside for shooting. This is a subject covered many times here on Another Bird Blog, in the birding press on a regular basis and in National newspapers on a number of occasions. As ever there is no interest from the UK Government or other parties to put a stop to an archaic practice that has such a devastating impact upon native species.
The BTO Atlas of 2013 tells me that the numbers of captive-bred Pheasants released into the wild has increased fivefold since the early 1960s to around 35 million birds annually. Some 15 million Pheasant are shot annually.
Captive Pheasant rearing
“High densities of Pheasants potentially have negative effects on native species, but these have been poorly studied. Indirect effects possibly include modification of the structure of the field layer, the spread of disease and parasites and competition for food. Recent research indicates that infection with caecal nematodes from farm-reared Pheasants may be contributing to the decline of Grey Partridge.”
Grey Partridge
When I watch hordes of young Pheasants thundering through late summer fields and woodland edge there is no doubt in my mind that their effect on the environment is wholly negative.
The BTO Atlas also states that there has been a 91% population decline of Grey Partridge in the UK between 1967-2010, during the Breeding Atlas of 1968-72 and the Breeding Atlas of 1988-91.
“Local extinctions may be masked in some areas by the release of captive-bred birds onto shooting estates: about 100,000 captive-reared Grey Partridges are released in Britain each year”. The Atlas gives no figures on the number of captive-bred birds subsequently shot for sport; neither does it give any indication of how any surviving birds impact upon any truly wild Grey Partridge population.
Given that the Grey Partridge is in any case a secretive and difficult species to study, any such investigation would by now be almost impossible to conduct.
The problem is further complicated by the release into the same environment of Red-legged Partridge, a picture I know only too well from local farms.
"As more farms diversify into shooting, the number of Red-legged Partridges released has increased and this is illustrated by the National Gamebag Census, where numbers shot quadrupled between 1990 and 2005 (Game & Wildlife Conservation Trust 2013). It is estimated that 6.5 million partridges (Grey and Red-legged) were released across the UK in 2004, and 2.6 million were shot. There has been little research on the impacts of released birds on native species, but there is some evidence that shooting operations based on large-scale releases of Red-legged Partridges could be implicated in local extinctions of Grey Partridges.”
Red-legged Partridge
To my unscientific but daily birding eyes that last sentence would seem to be a gross understatement.
At the end of the day there is one conclusion to be drawn from this now familiar, sorry story.
Nothing will change - just Follow The Money.
Linking this post to https://viewingnaturewitheileen.blogspot.com.




















































.JPG)



.JPG)







.jpg)











